介绍
之前的文章研究了点图、卡吉图和仁科图。一系列关于20世纪图表的文章不断发表。这次我们将讨论三行突破图,或者更准确地说,通过程序代码实现它们。关于这个图表的来源几乎没有什么信息。我想是从日本开始的。1994年史蒂夫·尼森在美国出版的《超越烛台》(超越烛台)。
除上述图表外,未提及三线突破图的建设时间框架。它基于确定时间框架内的最终收盘价,可以过滤与先前价格相比的小价格波动。
在史蒂夫·尼森的《超越烛台》(超越烛台)一书中,描述了绘制这幅图的11条原则(第185页)。我把它们合并成三个。
- 原则一:根据市场波动情况,选择初始价格,画出正负线。它将标记一个新的最小值或最大值。
- 原则二:当新价格低于最低或高于最高时,我们画一条正负线。
- 原则3:画一条与前一个运动方向相反的线必须穿过最低或最高的方向。同时,如果有多条相同的线,则最低或最高的计算基于其中两条线(如果有两条连续的相同线)或三条线(如果有三条或更多连续的相同线)。
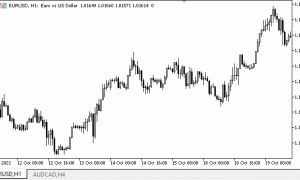
让我们仔细看看基于历史数据(图例)的构造图的经典示例。1)。
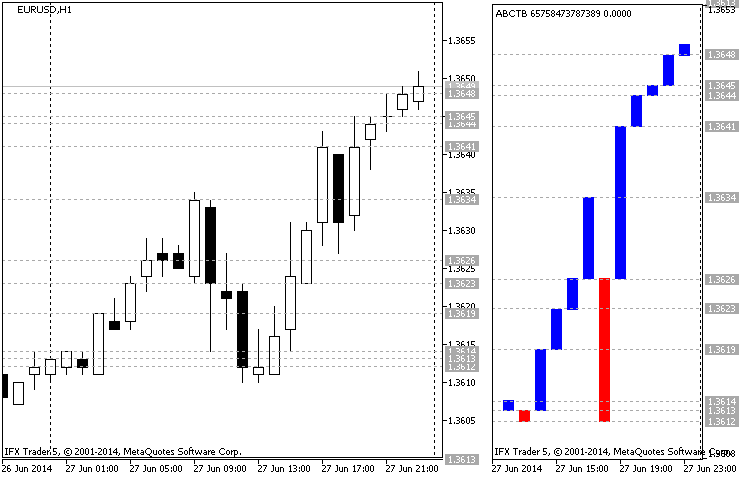
传说。1构建三线突破图的示例(2014年6月27日,欧元兑美元)
传说。1左边是烛光条形图,右边是三线突破图。这是时间框架为h1的欧元兑美元图表。图表起始日期为2014年6月27日,起始价格为1.3613(蜡烛结束时间为00:00),蜡烛结束时间为1.3614,形成三线突破图的第一条正线。然后短蜡烛(02:00)形成一条正线,收于1.3612点(收盘价低于前一个最低点)。
后来,多头烛台将价格推到了1.3619(03:00)的标记位置,形成了一个新的高点,以及一个柱线。04:00下降蜡烛线不低于最小值,不影响结构。蜡烛线在05:00关闭在1.3623,标志着一个新的高点(新的正极线)。
现在要继续向下的趋势,我们需要经历两个最低点(1.3613),但是公牛没有放弃他们的位置,因此形成了一个新的高点1.3626(06:00)。后来,多头试图扭转上涨趋势两个小时,但同样的趋势继续,达到了历史新高1.3634(09:00)。公牛队领先。现在通过三个最低价格(1.3626;1.3623和1.3619)画一条直线。
如我们所见,在接下来的三个小时内,空头头寸主导市场,并下跌至1.3612(12:00)。它体现了一条新的积极路线。然而,接下来的五个小时表明,多头正在重新赢得他们的头寸,并带领市场回到1.3641点,超过了之前的1.3626点的高点,在17点形成了一条新的积极线。空头头寸未能在18:00超越之前的低点,并在未来5小时内将市场引导至1.3649点,形成了每小时一个新的积极线。
图表构建基础
在我们得到代码之前,让我们先讨论一下度量标准本身,并找出它们的不同之处。与其他指标一样,第三线突破是显而易见的,旨在促进有效的市场分析和寻找新战略。我肯定你想知道这里有没有新的东西。事实上,还有一些。此索引可以更改计算的价格类型。它涵盖了所有四个标准价格条。建筑图表的经典设计仅适用于一种类型,而现代设计则适用于所有四种价格类型(开盘价、最高价、最低价和收盘价)。它通过添加“阴影”来修改经典图表结构的外观,使其看起来像日本烛台,即添加图表的视觉效果。
现代版本的特性还可以设置在缺少数据时同步价格数据的首选项。
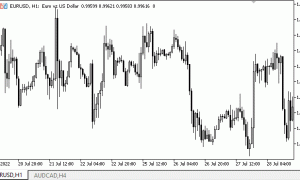
图表结构的现代类型如图2所示。
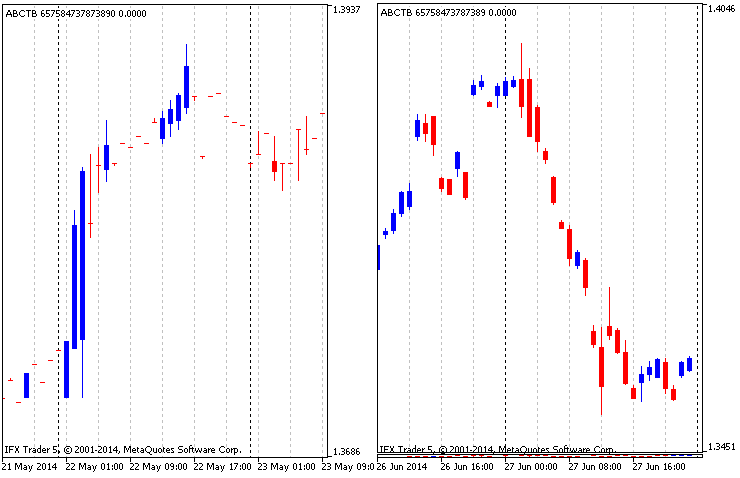
图形图例。2基于四种价格类型的修订图表
由于现代建筑结合了四种不同价格类型的三线突破图,自然可以发现价格之间的差异。为了避免出现这种情况,必须及时同步数据。价格同步带来两个变化:完成(图例。右侧2个)和部分(图例。左边2个)。完全同步表示一个过滤位置,其中所有数据都绘制在图上,丢失的数据被设置为指定的首选价格替换。在完全同步模式下,只需省略丢失的数据,并只绘制具有完整数据的蜡烛。
另一个创新是循环分离,这有助于信号分割。如您所知,周期分隔符可以在图表设置中启用。在指示器中,可以根据指定的设置更改时间范围。与MetaTrader 5中的图表不同,周期由垂直虚线分隔,该虚线由该指示器中褪色的垂直线(蜡烛、图例)表示。3):
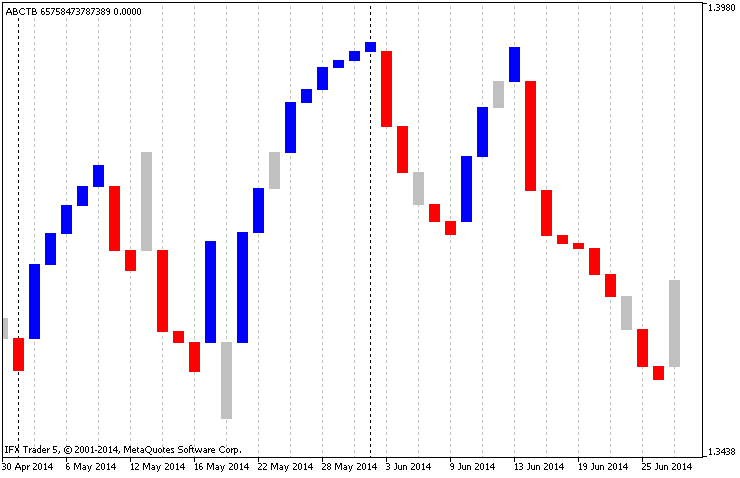
图形图例。索引3中的定期分隔符
此外,还增加了技术指标IMA,该指标是根据主表价格建立的,但可以及时与指标数据同步。因此,数据由平均线(图例)过滤。4):
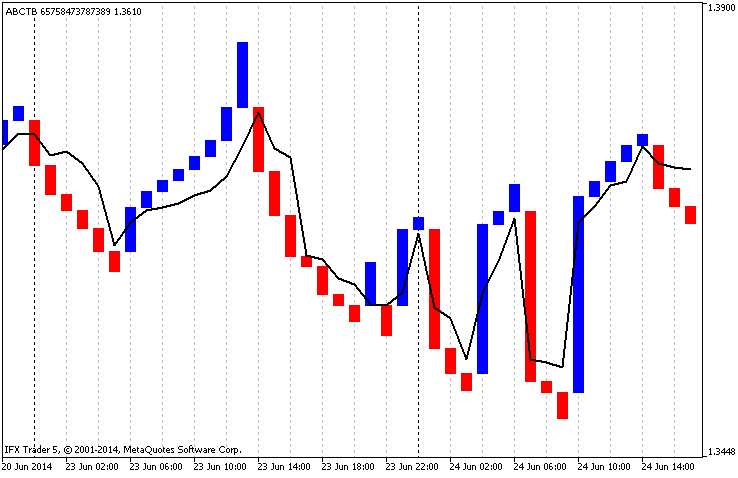
传说。4内部平均值
索引还具有一个功能,可以设置绘图的最小移动点数量和需要反转的线数量。它还充当过滤器。
索引代码
度量的算法非常简单。它有三个阶段:复制数据、基于复制数据计算和填充索引缓冲区(根据接收到的数据构建图表)。代码根据其内部和输入数据连接分为多个功能。让我们仔细看看代码。
1。指示器输入参数
索引的前言包含了图形结构的说明。有两个指标:图表“abctb”(绘制彩色蜡烛)和附加的平均线“line tlb”(绘制线)。因此,有六个缓冲区。以下枚举(枚举)类型用于改进接口设置和设置本身:
- magic_numb-magic number类型是long。它是表示指标的唯一数字。如果需要,可以将类型转换为带修改参数的字符串。
- 时间框架-计算时间范围,输入枚举时间框架,这是主要参数(指标时间框架);
- 时间重新绘制-图表更新周期,键入枚举时间范围。这是用于重新计算图表的时间范围。为了快速重新绘制表格,按下键盘上的“R”键-指示器的综合控制;
- first_date_start-开始日期,键入datetime。主要参数是数据复制和绘制的起点。
- 图表价格-计算的价格类型(0-收盘价,1-开盘价,2-最高价格,3-最低价格)。对于经典结构图,必须选择价格类型。如前所述,启用修改后的构造时将忽略此参数。
- step_min_f-绘制线条所需的新列的最小步长(>;0,类型int)或跳跃距离;
- line_to_back_f-显示反转的行数(>;0,键入int)。经典类型为显示反转建议三行。
- 图表类型-图表结构类型(0-经典,1-修改),类型选择。它是一种结构类型的开关。
- 图表颜色-新周期开始时的颜色变化(布尔类型)。用于在新周期开始时更改线条颜色;
- 图表同步-仅在完全同步的基础上构建图表(布尔型,如果为真,则在构建图表之前执行完全同步,并删除所有缺少的值);
- 图表优先级-收盘价优先级(类型选择,有四个更改。这意味着本地同步首先取收盘价,忽略了完整性。
- 图表优先开放价格优先。这里同样适用。
- 先列出最高价。这里同样适用。
- 先列出最低价格。这里同样适用。
- Ma_Draw-绘制平均值(布尔型,真,然后绘制平均值);
- Ma_Price-构造平均值的价格类型可以是枚举应用的价格之一。
- Ma_方法-构造类型,可以是Enum_Ma_方法之一;
- Ma_周期-平均周期;
然后我们声明缓存数组、变量和计算结构。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ABCTB.mq5 | //| "Azotskiy Aktiniy ICQ:695710750" | //| "" | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ // ABCTB - Auto Build Chart Three Line Break #property copyright "Azotskiy Aktiniy ICQ:695710750" #property link "" #property version "1.00" #property indicator_separate_window #property indicator_buffers 6 #property indicator_plots 2 //--- plot ABCTB #property indicator_label1 "ABCTB" #property indicator_type1 DRAW_COLOR_CANDLES #property indicator_color1 clrBlue,clrRed,clrGreenYellow #property indicator_style1 STYLE_SOLID #property indicator_width1 1 //--- plot LINE_TLB #property indicator_label2 "LINE_TLB" #property indicator_type2 DRAW_LINE #property indicator_color2 clrRed #property indicator_style2 STYLE_SOLID #property indicator_width2 1 //--- Price type for calculation enum type_price { close=0, // Close open=1, // Open high=2, // Hight low=3, // Low }; //--- type of chart construction enum type_build { classic=0, // Classic modified=1, // Modified }; //--- priority enum priority { highest_t=4, // Highest high_t=3, // High medium_t=2, // Medium low_t=1, // Low }; //--- input parameters input long magic_numb=65758473787389; // Magic number input ENUM_TIMEFRAMES time_frame=PERIOD_CURRENT; // Calculation time range input ENUM_TIMEFRAMES time_redraw=PERIOD_M1; // Period of chart updates input datetime first_date_start=D'2013.03.13 00:00:00'; // Start date input type_price chart_price=close; // Price type for calculation (0-Close, 1-Open, 2-High, 3-Low) input int step_min_f=4; // Minimum step for a new column (>0) input int line_to_back_f=3; // Number of lines to display a reversal(>0) input type_build chart_type=classic; // Type of chart construction (0-classic, 1-modified) input bool chart_color_period=true; // Changing color for a new period input bool chart_synchronization=true; // Constructing a chart only upon complete synchronization input priority chart_priority_close=highest_t; // Priority of the closing price input priority chart_priority_open=highest_t; // Priority of the opening price input priority chart_priority_high=highest_t; // Priority of the maximum price input priority chart_priority_low=highest_t; // Priority of the minimum price input bool ma_draw=true; // Draw the average input ENUM_APPLIED_PRICE ma_price=PRICE_CLOSE; // Price type for constructing the average input ENUM_MA_METHOD ma_method=MODE_EMA; // Construction type input int ma_period=14; // Averaging period //--- indicator buffers //--- buffer of the chart double ABCTBBuffer1[]; double ABCTBBuffer2[]; double ABCTBBuffer3[]; double ABCTBBuffer4[]; double ABCTBColors[]; //--- buffer of the average double LINE_TLBBuffer[]; //--- variables MqlRates rates_array[];// bar data array for analysis datetime date_stop; // current date datetime date_start; // start date variable for calculation //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Struct Line Price | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ struct line_price// structure for storing information about the past lines { double up; // value of the high price double down;// value of the low price }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Struct Line Information | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ struct line_info// structure for storing information about the shared lines { double up; double down; char type; datetime time; }; line_info line_main_open[]; // data on the opening prices chart line_info line_main_high[]; // data on the maximum prices chart line_info line_main_low[]; // data on the minimum prices chart line_info line_main_close[]; // data on the closing prices chart //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Struct Buffer Info | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ struct buffer_info// structure for storing data for filling a buffer { double open; double high; double low; double close; char type; datetime time; }; buffer_info data_for_buffer[];// data for filling the modified construction buffer datetime array_datetime[]; // array for storing information of the time for every line int time_array[3]; // array for the function func_date_color datetime time_variable; // variable for the function func_date_color bool latch=false; // variable-latch for the function func_date_color int handle; // handle of the indicator iMA int step_min; // variable of the minimum step int line_to_back; // variable of the number of lines to display a reversal
2。IT功能
所有指示器缓冲区都在函数OnInit中声明,并且指示器数组被设置为时间序列。
然后,我们设置不会反映在图表上的索引值,设置名称,指定准确性,并删除当前值,因为它们会导致图表过载。这里,我们还设置了索引IMA句柄并检查输入数据的正确性。如果出现错误,将输出相应的消息,并将值更改为最小值。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Custom indicator initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { //--- indicator buffers mapping //--- buffers for a chart SetIndexBuffer(0,ABCTBBuffer1,INDICATOR_DATA); ArraySetAsSeries(ABCTBBuffer1,true); SetIndexBuffer(1,ABCTBBuffer2,INDICATOR_DATA); ArraySetAsSeries(ABCTBBuffer2,true); SetIndexBuffer(2,ABCTBBuffer3,INDICATOR_DATA); ArraySetAsSeries(ABCTBBuffer3,true); SetIndexBuffer(3,ABCTBBuffer4,INDICATOR_DATA); ArraySetAsSeries(ABCTBBuffer4,true); SetIndexBuffer(4,ABCTBColors,INDICATOR_COLOR_INDEX); ArraySetAsSeries(ABCTBColors,true); //--- buffer for constructing the average SetIndexBuffer(5,LINE_TLBBuffer,INDICATOR_DATA); ArraySetAsSeries(LINE_TLBBuffer,true); //--- set the values that are not going to be reflected on the chart PlotIndexSetDouble(0,PLOT_EMPTY_VALUE,0); // for the chart PlotIndexSetDouble(1,PLOT_EMPTY_VALUE,0); // for the average //--- set the indicator appearance IndicatorSetString(INDICATOR_SHORTNAME,"ABCTB "+IntegerToString(magic_numb)); // name of the indicator //--- accuracy of display IndicatorSetInteger(INDICATOR_DIGITS,_Digits); //--- prohibit displaying the results of the indicator current value PlotIndexSetInteger(0,PLOT_SHOW_DATA,false); PlotIndexSetInteger(1,PLOT_SHOW_DATA,false); //--- handle=iMA(_Symbol,time_frame,ma_period,0,ma_method,ma_price); if(step_min_f<1) { step_min=1; Alert("Minimum step for a new column must be greater than zero"); } else step_min=step_min_f; //--- if(line_to_back_f<1) { line_to_back=1; Alert("The number of lines to display a reversal must be greater than zero"); } else line_to_back=line_to_back_f; //--- return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); }
三。重复的数据函数
由于指标设计适用于所有四种价格类型,因此复制所有数据(包括时间)至关重要。在MQL5中有一个名为mqlrates的结构。用于存储交易期间的开始时间、价格、数量和价差信息。
此函数的输入参数是开始和结束日期、时间帧和mqlrates类型的目标数组。如果复制成功,此函数将返回true。数据将被复制到中间数组。计算出的缺失数据加上一个句点将被复制到此点,数据将被永久更新。如果成功复制到中间数组,数据将被复制到数组,以确保函数正常工作。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Func All Copy | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool func_all_copy(MqlRates &result_array[],// response array ENUM_TIMEFRAMES period, // timeframe datetime data_start, // start date datetime data_stop) // end date { //--- declaration of auxiliary variables bool x=false; // variable for the function response int result_copy=-1; // copied data count //--- adding variables and arrays for calculation static MqlRates interim_array[]; // temporary dynamic array for storing copied data static int bars_to_copy; // number of bars for copying static int bars_copied; // number of copied bars since the start date //--- find out the current number of bars in the time range bars_to_copy=Bars(_Symbol,period,data_start,data_stop); //--- count the number of bars to be copied bars_to_copy-=bars_copied; //--- if it is not the first time when data is being copied if(bars_copied>0) { bars_copied--; bars_to_copy++; } //--- change the size of the receiving array ArrayResize(interim_array,bars_to_copy); //--- copy data to a temporary array result_copy=CopyRates(_Symbol,period,0,bars_to_copy,interim_array); //--- check the result of copying data if(result_copy!=-1) // if copying to the temporary array was successful { ArrayCopy(result_array,interim_array,bars_copied,0,WHOLE_ARRAY); // copy the data from the temporary array to the main one x=true; // assign the positive response to the function bars_copied+=result_copy; // increase the value of the copied data } //--- return(x); }
4。计算数据函数
该函数是数据计算的原型,用于构造经典的三线穿透图。如前所述,此函数只计算数据并将其插入到代码开头声明的结构类型行信息的指定数组中。
此函数包含两个其他函数:func_重新分组和func_insert。让我们开始看看它们:
4.1。重组功能
此函数在同一方向上重新组织连续线的信息。它受到传递给它的数组大小的限制,或者受到指示器设置参数line_to_back_f(显示反向行数)的精确值的限制。因此,每次控件传递到函数时,所有接收到的关于标记的数据都会向下移动一点,索引为0的行中都会填充新的值。
这就是如何存储突破所需行所需的信息(在三行的经典情况下)。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ // Func Regrouping | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void func_regrouping(line_price &input_array[],// array for regrouping double new_price, // new price value char type) // type of movement { int x=ArraySize(input_array);// find out the size of the array for regrouping for(x--; x>0; x--) // regrouping loop { input_array[x].up=input_array[x-1].up; input_array[x].down=input_array[x-1].down; } if(type==1) { input_array[0].up=new_price; input_array[0].down=input_array[1].up; } if(type==-1) { input_array[0].down=new_price; input_array[0].up=input_array[1].down; } }
4.2。插入函数
 ;此函数将值插入响应数组。代码很简单,不需要详细解释。nbsp;
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ // Func Insert | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void func_insert(line_info &line_m[], // target array line_price &line_i[], // source array int index, // array element being inserted char type, // type of the target column datetime time) // date { line_m[index].up=line_i[0].up; line_m[index].down=line_i[0].down; line_m[index].type=type; line_m[index].time=time; }
用于计算数据的函数通常分为三部分。在第一部分中,根据分析和操作员开关将数据复制到中间数组。只关注重复的价格。第二部分运行一个测试来计算数据数组所需的空间。然后,初始化并传递给函数进行响应的数据数组行_Main_Array[]进行更改。第三部分,依次填充调整数据数组。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Func Build Three Line Break | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void func_build_three_line_break(MqlRates &input_array[], // array for analysis char price_type, // type of the price under analysis (0-Close, 1-Open, 2-High, 3-Low) int min_step, // minimum step for drawing a line int line_back, // number of lines for a reversal line_info &line_main_array[]) // array for return (response) of the function { //--- calculate the size of the array for analysis int array_size=ArraySize(input_array); //--- extract data required for calculation to an intermediate array double interim_array[];// intermediate array ArrayResize(interim_array,array_size);// adjust the intermediate array to the size of the data switch(price_type) { case 0: // Close { for(int x=0; x<array_size; x++) { interim_array[x]=input_array[x].close; } } break; case 1: // Open { for(int x=0; x<array_size; x++) { interim_array[x]=input_array[x].open; } } break; case 2: // High { for(int x=0; x<array_size; x++) { interim_array[x]=input_array[x].high; } } break; case 3: // Low { for(int x=0; x<array_size; x++) { interim_array[x]=input_array[x].low; } } break; } //--- enter the variables for storing information about current situation line_price passed_line[];// array for storing information about the latest prices of the lines (type structure line_price) ArrayResize(passed_line,line_back+1); int line_calc=0;// number of lines int line_up=0;// number of the last ascending lines int line_down=0;// number of the last descending lines double limit_up=0;// upper limit necessary to pass double limit_down=0;// lower limit necessary to pass /* Fill variables informing of the current situation with the first values */ passed_line[0].up=interim_array[0]; passed_line[0].down=interim_array[0]; //--- start the first loop to calculate received data for filling a buffer for drawing for(int x=0; x<array_size; x++) { if(line_calc==0)// no lines have been drawn { limit_up=passed_line[0].up; limit_down=passed_line[0].down; if(interim_array[x]>=limit_up+min_step*_Point)// the upper limit has been passed { func_regrouping(passed_line,interim_array[x],1);// regroup line_calc++;// update the line counter line_up++; } if(interim_array[x]<=limit_down-min_step*_Point)// the lower limit has been passed { func_regrouping(passed_line,interim_array[x],-1);// regroup line_calc++;// update the line counter line_down++; } } if(line_up>line_down)// last ascending line (lines) { limit_up=passed_line[0].up; limit_down=passed_line[(int)MathMin(line_up,line_back-1)].down; if(interim_array[x]>=limit_up+min_step*_Point)// the upper limit has been passed { func_regrouping(passed_line,interim_array[x],1);// regroup line_calc++;// update the line counter line_up++; } if(interim_array[x]<limit_down)// the lower limit has been passed { func_regrouping(passed_line,interim_array[x],-1);// regroup line_calc++;// update the line counter line_up=0; line_down++; } } if(line_down>line_up)// last descending line (lines) { limit_up=passed_line[(int)MathMin(line_down,line_back-1)].up; limit_down=passed_line[0].down; if(interim_array[x]>limit_up)// the upper limit has been passed { func_regrouping(passed_line,interim_array[x],1);// regroup line_calc++;// update the line counter line_down=0; line_up++; } if(interim_array[x]<=limit_down-min_step*_Point)// the lower limit has been passed { func_regrouping(passed_line,interim_array[x],-1);// regroup line_calc++;// update the line counter line_down++; } } } ArrayResize(line_main_array,line_calc);// change the size of the target array //--- zeroise variables and fill with the the initial data line_calc=0; line_up=0; line_down=0; passed_line[0].up=interim_array[0]; passed_line[0].down=interim_array[0]; //--- start the second loop to fill a buffer for drawing for(int x=0; x<array_size; x++) { if(line_calc==0)// no lines have been drawn { limit_up=passed_line[0].up; limit_down=passed_line[0].down; if(interim_array[x]>=limit_up+min_step*_Point)// the upper limit has been passed { func_regrouping(passed_line,interim_array[x],1);// regroup func_insert(line_main_array,passed_line,line_calc,1,input_array[x].time); line_calc++;// update the line counter line_up++; } if(interim_array[x]<=limit_down-min_step*_Point)// the lower limit has been passed { func_regrouping(passed_line,interim_array[x],-1);// regroup func_insert(line_main_array,passed_line,line_calc,-1,input_array[x].time); line_calc++;// update the line counter line_down++; } } if(line_up>line_down)// last ascending line (lines) { limit_up=passed_line[0].up; limit_down=passed_line[(int)MathMin(line_up,line_back-1)].down; if(interim_array[x]>=limit_up+min_step*_Point)// the upper limit has been passed { func_regrouping(passed_line,interim_array[x],1);// regroup func_insert(line_main_array,passed_line,line_calc,1,input_array[x].time); line_calc++;// update the line counter line_up++; } if(interim_array[x]<limit_down)// the lower limit has been passed { func_regrouping(passed_line,interim_array[x],-1);// regroup func_insert(line_main_array,passed_line,line_calc,-1,input_array[x].time); line_calc++;// update the line counter line_up=0; line_down++; } } if(line_down>line_up)// last descending line (lines) { limit_up=passed_line[(int)MathMin(line_down,line_back-1)].up; limit_down=passed_line[0].down; if(interim_array[x]>limit_up)// the upper limit has been passed { func_regrouping(passed_line,interim_array[x],1);// regroup func_insert(line_main_array,passed_line,line_calc,1,input_array[x].time); line_calc++;// update the line counter line_down=0; line_up++; } if(interim_array[x]<=limit_down-min_step*_Point)// the lower limit has been passed { func_regrouping(passed_line,interim_array[x],-1);// regroup func_insert(line_main_array,passed_line,line_calc,-1,input_array[x].time); line_calc++;// update the line counter line_down++; } } } }
5。图表构造函数
此函数的目的是根据选定的构造参数(经典或修改的)计算图表数据并用显示数据填充索引缓冲区。与前面的函数一样,这个图构造函数有三个附加函数。它们是颜色函数、同步函数和平均函数。让我们更详细地讨论一下。
5.1。颜色函数
此函数只有一个输入参数-时间。函数的响应是一个布尔变量。如果传递的数据是周期的边界,则函数返回true。由于周期取决于所选的时间范围,因此函数通过条件运算符if具有内置的周期分隔。选择循环后,检查是否已启动新循环。它通过将日期转换为mqldatetime结构并进行比较来完成。对于大于或等于h2的时间范围,日期值的更改表示新周期的开始。从h12到d1的时间范围,包括月份变化,以及在w1和mn之间,我们检查年份变化。
不幸的是,结构mqldatetime不包含有关本周的信息。这个问题可以通过创建一个由可变时间变量表示的初始点来解决。沿着这条线前进,从这个日期开始扣除每周的秒数。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ // Func Date Color | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool func_date_color(datetime date_time) // input date { bool x=false;// response variable int seconds=PeriodSeconds(time_frame);// find out the calculation time range MqlDateTime date; TimeToStruct(date_time,date);// convert data if(latch==false) // check the state of the latch { MqlDateTime date_0; date_0=date; date_0.hour=0; date_0.min=0; date_0.sec=0; int difference=date_0.day_of_week-1; datetime date_d=StructToTime(date_0); date_d=date_d-86400*difference; time_variable=date_d; latch=true;// lock the latch } if(seconds<=7200)// period is less than or equal to H2 { if(time_array[0]!=date.day) { x=true; time_array[0]=date.day; } } if(seconds>7200 && seconds<=43200)// period is greater than H2 but less than or equal to H12 { if(time_variable>=date_time) { x=true; time_variable=time_variable-604800; } } if(seconds>43200 && seconds<=86400)// period is greater than H12 but less than or equal to D1 { if(time_array[1]!=date.mon) { x=true; time_array[1]=date.mon; } } if(seconds>86400)// period W1 or MN { if(time_array[2]!=date.year) { x=true; time_array[2]=date.year; } } return(x); }
5.2。同步功能
同步函数有六个输入参数:四个是优先级,布尔参数是完全或部分同步,以及它自己的分析数组。该功能分为两部分:完全同步和局部同步。
完全同步的三个阶段:
- 计算数组元素以满足包含数据的所有四种价格类型。
- 在相同的条件下,元素被复制到中间数组。
- 从中间数组复制并将其作为参数传递。
本地同步更复杂。
传递一维数组的数组并将其转换为二维数组,其中第一个索引表示顺序,第二个是价格类型。然后我们介绍一个包含四个元素的一维数组。将价格优先级复制到数组,然后对数组进行排序以确定优先级。然后,我们使用循环for和条件运算符if根据优先级进行分配。同时,如果优先级相同,则价格顺序如下:关闭、打开、最高和最低。一旦运算符if找到第一个优先级值,则的循环将替换先前创建的二维数组中的所有零值,依此类推。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ // Func Synchronization | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void func_synchronization(buffer_info &info[], bool synchronization, char close, char open, char high, char low) { if(synchronization==true)// carry out a complete synchronization { int calc=0;// count variable for(int x=0; x<ArraySize(info); x++)// count complete data { if(info[x].close!=0 && info[x].high!=0 && info[x].low!=0 && info[x].open!=0)calc++; } buffer_info i_info[]; // enter a temporary array for copying ArrayResize(i_info,calc);// change the size of the temporary array calc=0; for(int x=0; x<ArraySize(info); x++)// copy data into the temporary array { if(info[x].close!=0 && info[x].high!=0 && info[x].low!=0 && info[x].open!=0) { i_info[calc]=info[x]; calc++; } } ZeroMemory(info); // clear the target array ArrayResize(info,calc); // change the size of the main array for(int x=0; x<calc; x++)// copy data from the temporary array to the main one { info[x]=i_info[x]; } } if(synchronization==false) // change zero values to priority ones { int size=ArraySize(info); // measure the size of the array double buffer[][4]; // create a temporary array for calculation ArrayResize(buffer,size); // change the size of the temporary array for(int x=0; x<size; x++) // copy data into the temporary array { buffer[x][0]=info[x].close; buffer[x][1]=info[x].open; buffer[x][2]=info[x].high; buffer[x][3]=info[x].low; } char p[4];// enter an array for sorting by the order p[0]=close; p[1]=open; p[2]=high; p[3]=low;// assign variables for further sorting ArraySort(p); // sort int z=0,v=0; // initialize frequently used variables for(int x=0; x<4; x++)// taking into account the results of the sorting, look through all variables and substitute them according to the priority { if(p[x]==close)// priority is for the closing prices { for(z=0; z<size; z++) { for(v=1; v<4; v++) { if(buffer[z][v]==0)buffer[z][v]=buffer[z][0]; } } } if(p[x]==open)// priority is for the opening prices { for(z=0; z<size; z++) { for(v=0; v<4; v++) { if(v!=1 && buffer[z][v]==0)buffer[z][v]=buffer[z][1]; } } } if(p[x]==high)// priority is for the maximum prices { for(z=0; z<size; z++) { for(v=0; v<4; v++) { if(v!=2 && buffer[z][v]==0)buffer[z][v]=buffer[z][2]; } } } if(p[x]==low)// priority is for the minimum prices { for(z=0; z<size; z++) { for(v=0; v<3; v++) { if(buffer[z][v]==0)buffer[z][v]=buffer[z][3]; } } } } for(int x=0; x<size; x++)// copy data from the temporary array back { info[x].close=buffer[x][0]; info[x].open=buffer[x][1]; info[x].high=buffer[x][2]; info[x].low=buffer[x][3]; } } }
5.3。平均线函数
这是最简单的函数。使用OnInit函数中接收的索引句柄,我们复制与传递给函数的参数日期相对应的值。然后,该值作为响应返回给函数。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ // Func MA | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double func_ma(datetime date) { double x[1]; CopyBuffer(handle,0,date,1,x); return(x[0]); }
绘制图形的功能通常分为两部分:经典绘制和修改。该函数有两个输入参数:用于构造的价格类型(在修改模式中被忽略)和构造类型(经典和修改)。
首先清除指示缓冲器,然后根据施工类型分为两部分。第一部分(我们正在讨论的修改结构)开始调用这个函数来计算所有四种价格类型。然后,我们创建一个通用的数据数组,即复制使用的数据并接收由调用函数计算的数据。然后,对接收到的数据数组进行排序,并清除复制的数据。在全局级别为_buffer[]声明数组数据_之后,将填充基于与以下数据同步的连续日期。填充索引缓冲区是修改构造的最后一个阶段。
第二部分(经典结构)要简单得多。首先调用数据计算函数,然后填充索引缓冲区。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Func Chart Build | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void func_chart_build(char price, // price type for chart construction char type) // type of chart construction { //--- Zeroise the buffers ZeroMemory(ABCTBBuffer1); ZeroMemory(ABCTBBuffer2); ZeroMemory(ABCTBBuffer3); ZeroMemory(ABCTBBuffer4); ZeroMemory(ABCTBColors); ZeroMemory(LINE_TLBBuffer); if(type==1)// construct a modified chart (based on all price types) { func_build_three_line_break(rates_array,0,step_min,line_to_back,line_main_close);// data on closing prices func_build_three_line_break(rates_array,1,step_min,line_to_back,line_main_open);// data on opening prices func_build_three_line_break(rates_array,2,step_min,line_to_back,line_main_high);// data on maximum prices func_build_three_line_break(rates_array,3,step_min,line_to_back,line_main_low);// data on minimum prices //--- calculate data arrays int line_main_calc[4]; line_main_calc[0]=ArraySize(line_main_close); line_main_calc[1]=ArraySize(line_main_open); line_main_calc[2]=ArraySize(line_main_high); line_main_calc[3]=ArraySize(line_main_low); //--- gather the date array int all_elements=line_main_calc[0]+line_main_calc[1]+line_main_calc[2]+line_main_calc[3];// find out the number of all elements datetime datetime_array[];// enter the array for copying ArrayResize(datetime_array,all_elements); int y[4]; ZeroMemory(y); for(int x=0;x<ArraySize(datetime_array);x++)// copy data into the array { if(x<line_main_calc[0]) { datetime_array[x]=line_main_close[y[0]].time; y[0]++; } if(x<line_main_calc[0]+line_main_calc[1] && x>=line_main_calc[0]) { datetime_array[x]=line_main_open[y[1]].time; y[1]++; } if(x<line_main_calc[0]+line_main_calc[1]+line_main_calc[2] && x>=line_main_calc[0]+line_main_calc[1]) { datetime_array[x]=line_main_high[y[2]].time; y[2]++; } if(x>=line_main_calc[0]+line_main_calc[1]+line_main_calc[2]) { datetime_array[x]=line_main_low[y[3]].time; y[3]++; } } ArraySort(datetime_array);// sort the array //--- delete replicated data from the array int good_info=1; for(int x=1;x<ArraySize(datetime_array);x++)// count useful information { if(datetime_array[x-1]!=datetime_array[x])good_info++; } ArrayResize(array_datetime,good_info); array_datetime[0]=datetime_array[0];// copy the first element as it is the pattern in the beginning of comparison good_info=1; for(int x=1;x<ArraySize(datetime_array);x++)// fill the new array with useful data { if(datetime_array[x-1]!=datetime_array[x]) { array_datetime[good_info]=datetime_array[x]; good_info++; } } //--- fill the buffer for drawing (colored candles) int end_of_calc[4];// variables of storing information about the last comparison ZeroMemory(end_of_calc); ZeroMemory(data_for_buffer); ArrayResize(data_for_buffer,ArraySize(array_datetime));// change the size of the declared global array for storing data before passing it to a buffer for(int x=0; x<ArraySize(array_datetime); x++) { data_for_buffer[x].time=array_datetime[x]; for(int s=end_of_calc[0]; s<line_main_calc[0]; s++) { if(array_datetime[x]==line_main_close[s].time) { end_of_calc[0]=s; if(line_main_close[s].type==1)data_for_buffer[x].close=line_main_close[s].up; else data_for_buffer[x].close=line_main_close[s].down; break; } } for(int s=end_of_calc[1]; s<line_main_calc[1]; s++) { if(array_datetime[x]==line_main_open[s].time) { end_of_calc[1]=s; if(line_main_open[s].type==1)data_for_buffer[x].open=line_main_open[s].down; else data_for_buffer[x].open=line_main_open[s].up; break; } } for(int s=end_of_calc[2]; s<line_main_calc[2]; s++) { if(array_datetime[x]==line_main_high[s].time) { end_of_calc[2]=s; data_for_buffer[x].high=line_main_high[s].up; break; } } for(int s=end_of_calc[3]; s<line_main_calc[3]; s++) { if(array_datetime[x]==line_main_low[s].time) { end_of_calc[3]=s; data_for_buffer[x].low=line_main_low[s].down; break; } } } //--- start the function of synchronizing data func_synchronization(data_for_buffer,chart_synchronization,chart_priority_close,chart_priority_open,chart_priority_high,chart_priority_low); //--- preparatory actions before starting the function func_date_color ZeroMemory(time_array); time_variable=0; latch=false; //--- fill the buffer for drawing candles for(int x=ArraySize(data_for_buffer)-1,z=0; x>=0; x--) { ABCTBBuffer1[z]=data_for_buffer[x].open; ABCTBBuffer2[z]=data_for_buffer[x].high; ABCTBBuffer3[z]=data_for_buffer[x].low; ABCTBBuffer4[z]=data_for_buffer[x].close; if(ABCTBBuffer1[z]<=ABCTBBuffer4[z])ABCTBColors[z]=0; if(ABCTBBuffer1[z]>=ABCTBBuffer4[z])ABCTBColors[z]=1; if(func_date_color(data_for_buffer[x].time)==true && chart_color_period==true)ABCTBColors[z]=2; if(ma_draw==true)LINE_TLBBuffer[z]=func_ma(data_for_buffer[x].time); z++; } } else// construct a classic chart (based on one price type) { func_build_three_line_break(rates_array,price,step_min,line_to_back,line_main_close);// find data on selected prices ArrayResize(array_datetime,ArraySize(line_main_close)); //--- preparatory actions before starting the function func_date_color ZeroMemory(time_array); time_variable=0; latch=false; //--- the buffer for drawing candles for(int x=ArraySize(line_main_close)-1,z=0; x>=0; x--) { ABCTBBuffer1[z]=line_main_close[x].up; ABCTBBuffer2[z]=line_main_close[x].up; ABCTBBuffer3[z]=line_main_close[x].down; ABCTBBuffer4[z]=line_main_close[x].down; if(line_main_close[x].type==1)ABCTBColors[z]=0; else ABCTBColors[z]=1; if(func_date_color(line_main_close[x].time)==true && chart_color_period==true)ABCTBColors[z]=2; if(ma_draw==true)LINE_TLBBuffer[z]=func_ma(line_main_close[x].time); z++; } } }
6。积分函数
此功能结合了所有控制指示器元素。首先定义当前日期,然后调用复制数据函数和图形构造函数。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Func Consolidation | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void func_consolidation() { //--- defining the current date date_stop=TimeCurrent(); //--- copying data for analysis func_all_copy(rates_array,time_frame,first_date_start,date_stop); //--- basic construction of the chart func_chart_build(chart_price,chart_type); ChartRedraw(); }
7。键盘控制和自动控制构造函数
这些功能旨在通过键盘上的“R”键或根据选定的时间范围(OnCalculate)自动重新绘制度量。后者通过一个新的列函数(func_new_bar)进行分析,这是前面描述的is new bar函数的简化版本。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Custom indicator iteration function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnCalculate(const int rates_total, const int prev_calculated, const int begin, const double &price[]) { //--- if(func_new_bar(time_redraw)==true) { func_consolidation(); }; //--- return value of prev_calculated for next call return(rates_total); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ChartEvent function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnChartEvent(const int id, const long &lparam, const double &dparam, const string &sparam) { //--- event of a keystroke if(id==CHARTEVENT_KEYDOWN) { if(lparam==82) //--- the key "R" has been pressed { func_consolidation(); } } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Func New Bar | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool func_new_bar(ENUM_TIMEFRAMES period_time) { //--- static datetime old_times; // variable of storing old values bool res=false; // variable of the analysis result datetime new_time[1]; // time of a new bar //--- int copied=CopyTime(_Symbol,period_time,0,1,new_time); // copy the time of the last bar to the cell new_time //--- if(copied>0) // everything is ок. data copied { if(old_times!=new_time[0]) // if the old time of the bar is not equal to the new one { if(old_times!=0) res=true; // if it is not the first start, then new bar = true old_times=new_time[0]; // remember the time of the bar } } //--- return(res); }
此时,我们必须完成描述度量的代码,并讨论如何使用它。
使用指标和交易策略的示例
让我们从分析基于经典图构造的主要策略开始。
1。白线和黑线作为交易信号
一般来说,我们可以讨论两个规则:
- 规则一:买,当三个连续的正行;卖,当三个连续的负行。三条连续的线表明这一趋势正在出现。
- 规则2:当反向线低于三条连续正线时卖出;当反向线高于三条连续负线时买入。
让我们来看看传奇。6,显示了2013年开始的欧元兑美元的经典结构(分析的时间范围如图所示)。5)。
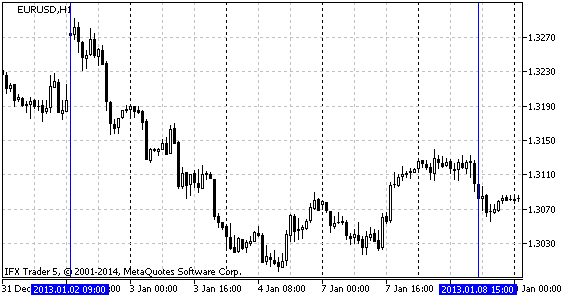
传说。5分析时间范围欧元兑美元h1
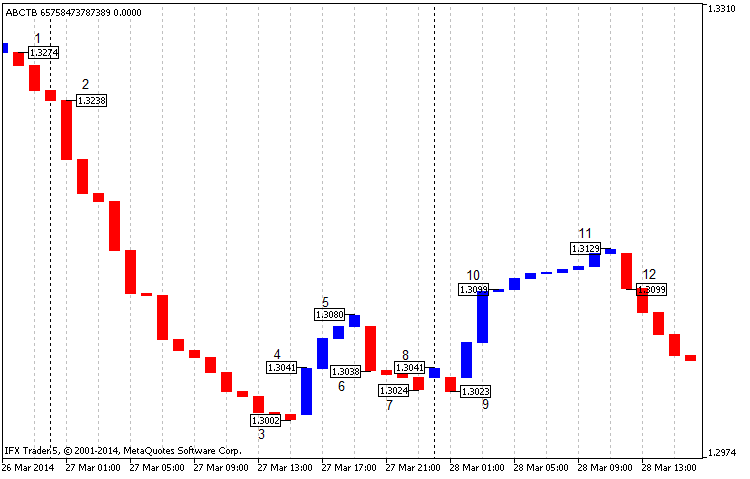
图例6三线突破图经典建筑欧元兑美元h1,从2013年开始,收盘价
在图表上(图例。6),我们可以清楚地看到1点和2点之间的信号(规则1),即起始卖点。在这种情况下,根据四位数的报价,收入超过200分。随后的第4点表示有利的购买(规则2)。截至收盘时,5点的利润为40点,而我们的盈亏平衡点为6点。
在第6点,我们可以看到销售信号(规则2)。在收盘点7,我们获得了10点的利润,在收盘点8,我们获得了盈亏平衡的利润。第8点和第9点不能被视为信号,因为它们既不满足规则1也不满足规则2。我们可以在第10点(规则1)买入;我们也可以在收盘价11时获利20点,或者在第12点盈亏平衡。所有数字都是四舍五入的。
在最好的情况下,使用这个策略,我们可以产生270个利润点,这是令人印象深刻的。同时,在一定的时间范围内,存在着一种强烈的趋势,影响着利润。在最坏的情况下,交易可能导致盈亏平衡,这并不坏。
值得一提的是,当情况同时符合规则1和规则2时,我们需要等待一行的确认,该行表示趋势在同一趋势中的逆转。
2。等距通道、支撑和阻力线
另一个交易策略是使用三线突破图进行技术分析。让我们看一下插图。7:
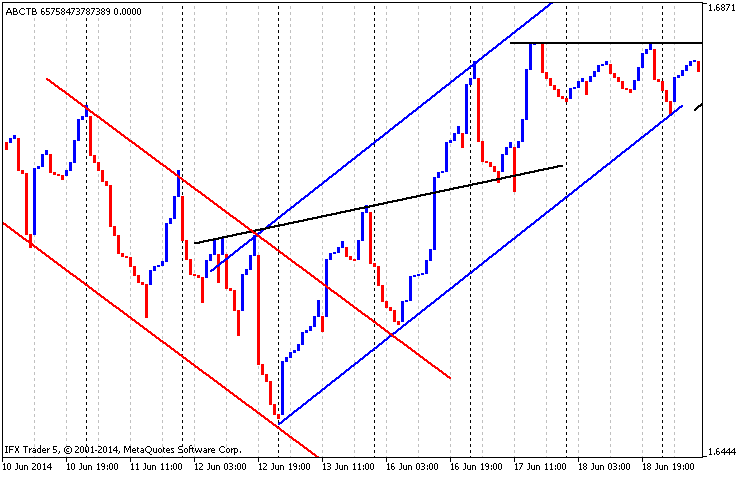
传说。7等距通道、支撑和阻力线,1英镑/美元,时间范围:2014年3月1日至2014年5月1日
在图7中,可以看到下降等距通道用红线绘制,上升等距通道用蓝色绘制,支撑和阻力线用黑色绘制。显然,第一条阻力线进入了支撑线。
三。烛形
从2013年开始,一个修改过的图表(两行突破)的时间框架为M30,货币对为USDCA,看起来很有趣。
我们可以把日本烛台的形状作为一个合理的信号(传说)。8)。
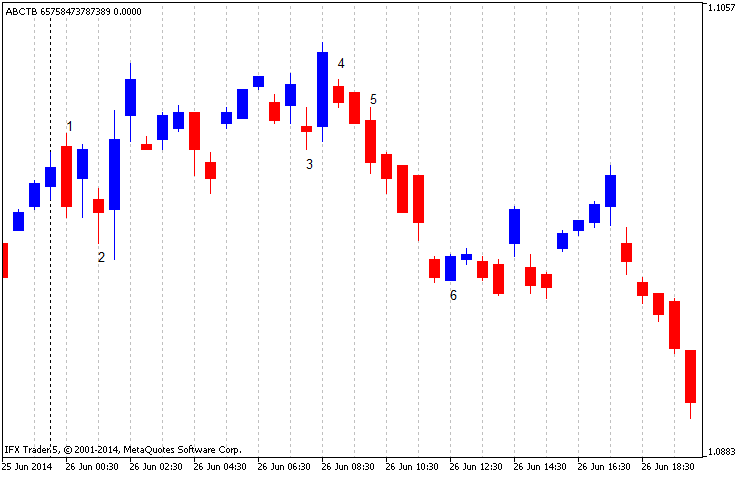
传说。8修订的三线突破图,USDCAD M30,从2013年开始,两线突破
在图表的开头,我们可以看到倒形“吞没”位于标记1的下方。它由两个烛台组成:前面是红色和蓝色。在上升趋势线之后,市场跌到了第二位,一种烛台反转形式的“锤子”。此时,市场转向。同样的情况也发生在表3中(“陀螺——陀螺”)。然后,倒装形式“kharami”(位置4)显示为烛台4和旁边的长阳线。形式6也由两个烛台组成(形式“吞噬-吞噬”),但与第一个类似的模式不同,它在相反的方向上逆转了市场。
因此,可以得出结论,使用该指标分析是可以接受的,但它存在信号较少和可能出现的显著退出等缺点。当然,这一战略需要进一步发展。
4。移动平均数
局部修改,例如添加移动平均线和只绘制直线,可以为分析提供新的机会。
让我们看一下插图。9:
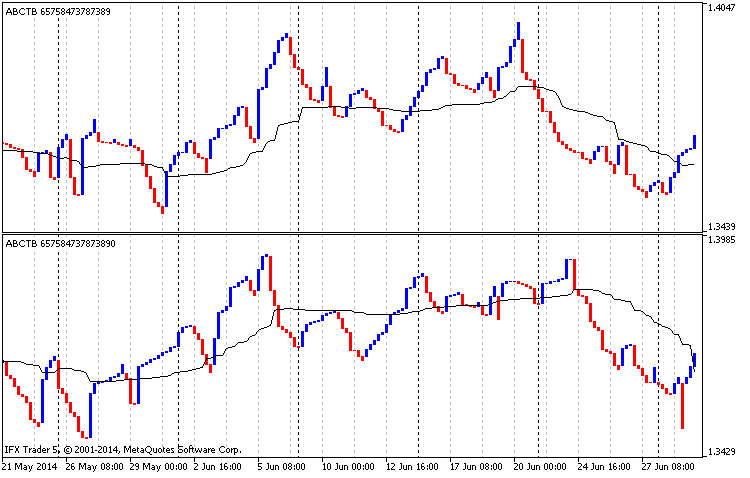
传说。9 2014年1月1日至2014年7月1日移动平均线、欧元兑美元h4、三线突破图、经典结构分析
在图9的上半部分,描述了给出最高价格的经典施工图,以及平均线(平均周期为90,最低价格,平滑平均)。图的下半部分显示了基于最低价格的经典施工图,以及平均线(平均周期为90,最高价格,平滑平均)。
因此,在图9的上半部分,平均值可被视为支撑线,而在下半部分,则相反,是阻力线。如果两个图表中的价格都低于平均水平,市场就处于下降趋势,目前最好卖出。当价格高于平均水平时,是时候买了。这种策略的一个缺点是它只适用于长期交易。
结论
最后,我可以说三线中断图总是给出一个好的信号,或者最坏情况下会导致收支平衡。实践证明,在长期趋势中最好使用此图表,因此我不建议在短期交易中使用此图表。如果有人对如何使用它进行交易有了新的想法,我很乐意讨论。
通常,我试图详细地揭示代码。第三,如果您对扩展、返工或优化有任何想法,请在本文档上发表评论。
本文由MetaQuotes Software Corp.翻译自俄语原文
,网址为https://www.mql5.com/ru/articles/902。
MyFxtop迈投(www.myfxtop.com)-靠谱的外汇跟单社区,免费跟随高手做交易!
免责声明:本文系转载自网络,如有侵犯,请联系我们立即删除,另:本文仅代表作者个人观点,与迈投财经无关。其原创性以及文中陈述文字和内容未经本站证实,对本文以及其中全部或者部分内容、文字的真实性、完整性、及时性本站不作任何保证或承诺,请读者仅作参考,并请自行核实相关内容。
著作权归作者所有。
商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。